Question
Rank the following solutions in order from most acidic to least acidic. A) HNO3>HNO2>NaNO3>NaNO2
Answer
Step 1
Given, Rank the following solutions in order from most acidic to least acidic.
Explanation:
We know that , As the acidity of any acid is determined by their capacity to give H+ ion and the then by stability of conjugate base after donating H+ the more stable the conjugate base more acidic the molecule will be.

Step 2
Salts of strong acid and strong base have pH =7 means these are neutral salt ,
And Salts of weak acid and strong base have pH >7 means these are basic in nature
Thus NaNO3 is more acidic than NaNO2

Answer
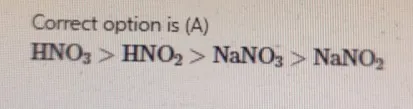
Table of Contents
Acidic Comparison: HNO3 vs HNO2 vs NaNO3 vs NaNO2
Introduction
Acidity is a fundamental concept in chemistry, pivotal for understanding the behavior of substances in various environments. In this article, we delve into an acidity comparison of four compounds: HNO3 (Nitric Acid), HNO2 (Nitrous Acid), NaNO3 (Sodium Nitrate), and NaNO2 (Sodium Nitrite). By examining their properties, we can rank these solutions from most acidic to least acidic, providing insights into their chemical behavior and practical applications.
Understanding Acidity
Acidity is determined by the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) in a solution. Strong acids dissociate completely in water, releasing a high concentration of H+ ions, while weak acids only partially dissociate. Salts, on the other hand, do not typically affect the acidity unless they hydrolyze to form acidic or basic solutions.
The Contenders
HNO3 (Nitric Acid):
- Properties: A strong acid, fully dissociating in water to release a high concentration of H+ ions.
- Reaction: HNO3 → H+ + NO3−
- Acidity Level: Very high, making it one of the strongest common acids used in laboratories and industry.
HNO2 (Nitrous Acid):
- Properties: A weak acid, partially dissociating in water.
- Reaction: HNO2 ⇌ H+ + NO2−
- Acidity Level: Moderate, less acidic than HNO3 due to partial dissociation.
NaNO3 (Sodium Nitrate):
- Properties: A neutral salt, derived from the strong acid HNO3 and the strong base NaOH.
- Reaction: NaNO3 → Na+ + NO3− (No H+ ions released)
- Acidity Level: Neutral, it does not contribute to the acidity or basicity of the solution.
NaNO2 (Sodium Nitrite):
- Properties: A salt derived from the weak acid HNO2 and the strong base NaOH.
- Reaction: NaNO2 → Na+ + NO2− (NO2− can slightly hydrolyze to form OH− ions, making the solution slightly basic)
- Acidity Level: Slightly basic, as it tends to increase the pH slightly due to hydrolysis.
Ranking the Acidity
Based on the properties and reactions of these compounds, we can rank them in order from most acidic to least acidic:
- HNO3 (Nitric Acid): As a strong acid, HNO3 dissociates completely in water, releasing the highest concentration of H+ ions. This makes it the most acidic solution among the four.
- HNO2 (Nitrous Acid): HNO2, being a weak acid, only partially dissociates, leading to a moderate acidity level. It is significantly less acidic than HNO3 but still releases H+ ions into the solution.
- NaNO3 (Sodium Nitrate): NaNO3 is a neutral salt and does not affect the acidity or basicity of the solution. It remains neutral when dissolved in water.
- NaNO2 (Sodium Nitrite): NaNO2, although a salt, can hydrolyze slightly to produce OH− ions, making the solution slightly basic. Therefore, it is the least acidic (or slightly basic) among the four compounds.
Applications and Implications
Understanding the acidity of these compounds is crucial for their application in various fields:
- HNO3 (Nitric Acid): Widely used in fertilizers, explosives, and as a strong oxidizing agent in chemical synthesis.
- HNO2 (Nitrous Acid): Used in organic synthesis and diazotization reactions, though less common due to its instability.
- NaNO3 (Sodium Nitrate): Commonly used in food preservation, fertilizers, and as a component in glass and ceramics.
- NaNO2 (Sodium Nitrite): Utilized in food preservation, particularly in curing meats, and in some industrial processes.
Conclusion
By comparing the acidity of HNO3, HNO2, NaNO3, and NaNO2, we can rank them from most acidic to least acidic. HNO3 stands out as the most acidic due to its complete dissociation, followed by the moderately acidic HNO2. NaNO3 is neutral, and NaNO2 is slightly basic due to hydrolysis. Understanding these differences is essential for their effective use in various chemical applications and industries.




